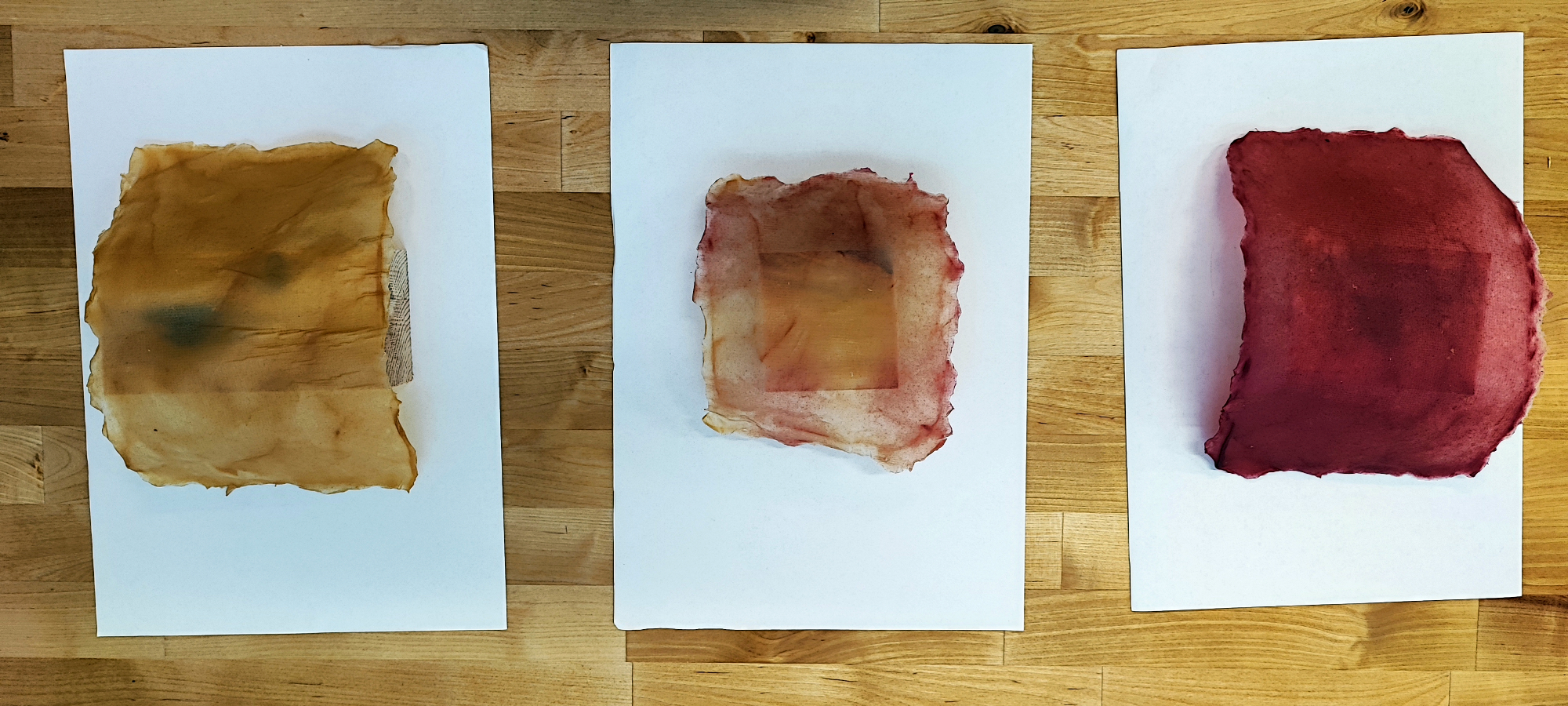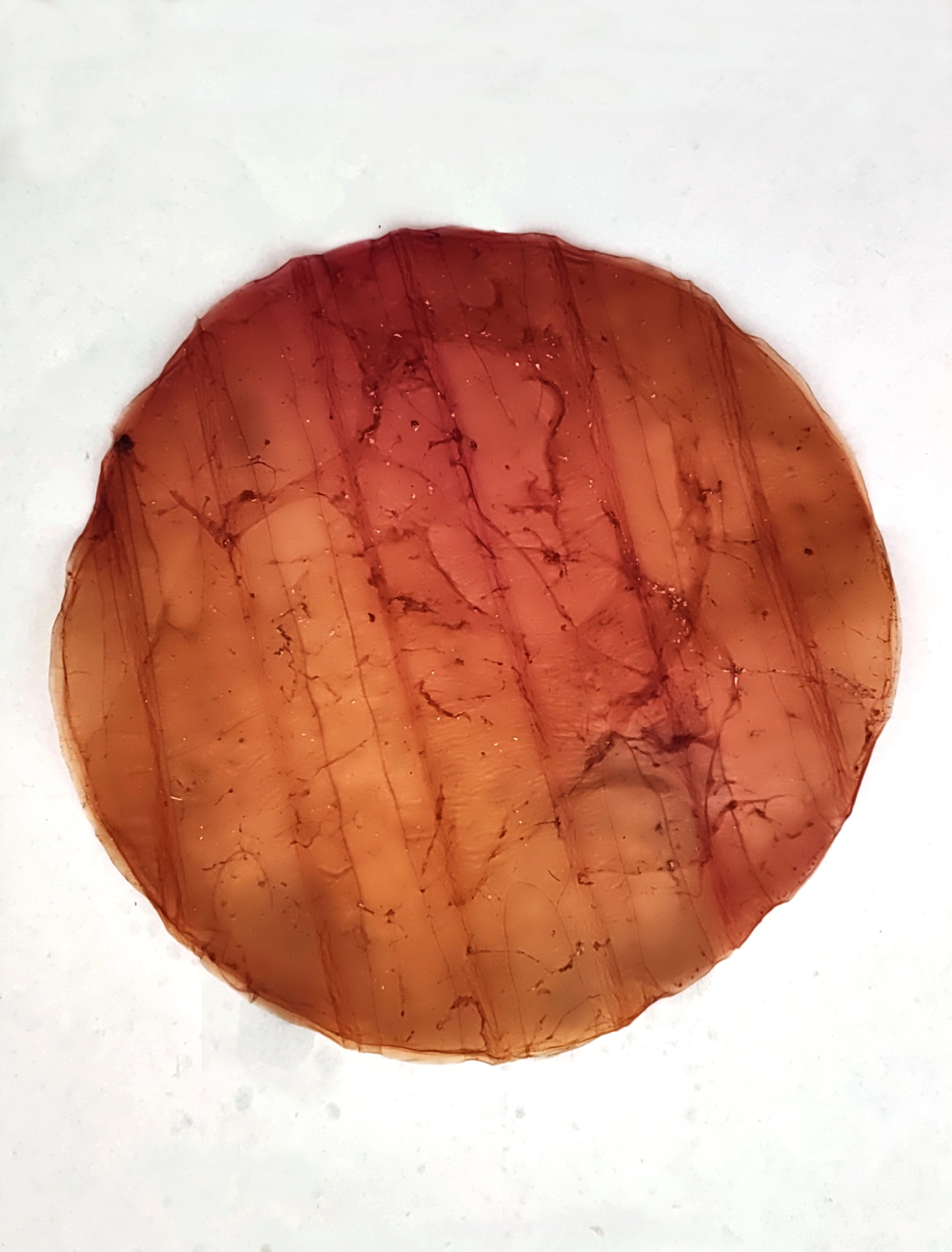
Scoby
bacterial celluloseOne of the best biomaterials is bacterial cellulose (BC). There are several ways to produce BC.
Bacterial cellulose, BC-derived biomaterials and composites have been extensively studied in the last decades due to possibility of obtaining new structures with remarkable properties.
In this case , we use BC produced by symbiotic colony of bacteria and yeasts named SCOBY.
This production method is more accessible, does not require the availability of a specific bacterial strain and can be carried out even in domestic conditions.
Scoby biofilm forms naturally as a byproduct during the juice fermentation or kombucha beverage fermentation process, and is observed as a film at the air-liquid interface. In terms of composition and structure, the biopolymer corresponds to cellulose. The composition of the microbial population in SCOBY can vary depending on its origin, geographical location, climate and the medium used for the fermentation process.
![]()
Bacterial cellulose, BC-derived biomaterials and composites have been extensively studied in the last decades due to possibility of obtaining new structures with remarkable properties.
In this case , we use BC produced by symbiotic colony of bacteria and yeasts named SCOBY.
This production method is more accessible, does not require the availability of a specific bacterial strain and can be carried out even in domestic conditions.
Scoby biofilm forms naturally as a byproduct during the juice fermentation or kombucha beverage fermentation process, and is observed as a film at the air-liquid interface. In terms of composition and structure, the biopolymer corresponds to cellulose. The composition of the microbial population in SCOBY can vary depending on its origin, geographical location, climate and the medium used for the fermentation process.